There are many reasons why Canadians leave the country permanently. Maybe you’re returning to your home country, or there are opportunities elsewhere. Or, you might just be tired of shovelling snow off the driveway every winter, and Florida seems like a better place to spend your golden years.
Whatever the case, numerous tax and legal considerations exist when you leave Canada — especially in the home selling process.
In this article, we talk about the many aspects of selling your home as you leave Canada and what you should consider.
Non-Resident Status
When you leave Canada to live in another country, you sever residential ties in Canada. This could mean selling your home, revoking your driver’s licence, or leaving clubs and organizations. As a result, you usually become a non-resident of Canada.
You become a non-resident for income tax purposes at the latest of:
- The date you leave
- The date your spouse or common-law partners and dependents leave Canada
- The date you become a resident of the country you settle in.
As a result, you aren’t obliged to pay all the same Canadian taxes as before. When you leave Canada, it’s best to speak with a tax professional to understand your obligations.
Departure Tax
One implication of becoming a non-resident is departure taxes — various taxes you must pay due to your departure.
When you leave Canada, the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) deems you to dispose of certain types of assets at fair market value and reacquire them at the same price. This creates a capital gains tax that you need to pay. Accountants generally refer to this as a deemed disposition.
This deemed disposition on departure applies to properties like jewellery, paintings, and company shares (excluding TFSA or RRSP shares). So, your home is not deemed to be sold when you leave the country.
How to Notify CRA that You’re Leaving Canada for Good and File Your Canada Departure Tax Return
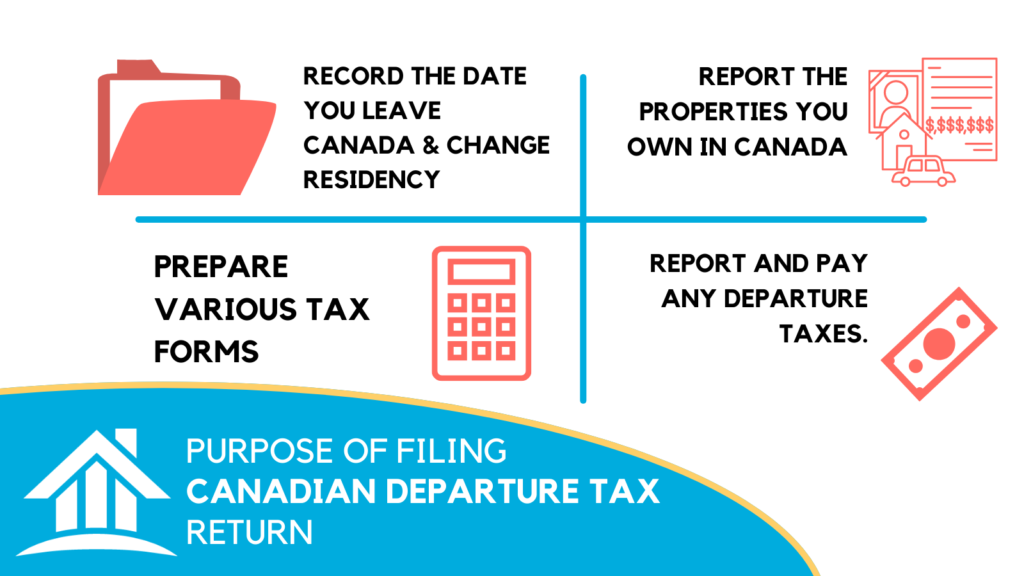
When you leave Canada, you need to file a departure tax return to notify CRA that you’re leaving. You generally need to file this tax return by April 30th of the year following your departure. The purpose of this tax return is to
- Record the date you leave Canada and change your residency
- Report the properties you own in Canada
- Prepare various tax forms
- Report and pay any departure taxes.
Leaving Canada and Your Principal Property
Capital gains are only taxable if you sell your home — suggesting it’s your principal property — when you’re no longer a resident. While, if you’re a resident, capital gains tax is generally exempt because your home is your principal residence.
When you depart from Canada, you usually have two options to deal with your principal property:
- Sell your property while you’re still a resident of Canada and have capital gains exempted through the principal residence exemption.
- Wait until you’re a non-resident to sell. In this case, the principal residence exemption is still generally available for the years in which you owned the property as a Canadian resident and fulfilled the other criteria for the principal residence exemption.
Selling Your Home as a Non-Resident
As a non-resident selling your home, you are liable to capital gains taxes because non-residents cannot access a principal residence exemption. In this process, you must notify CRA and complete Form T2062.
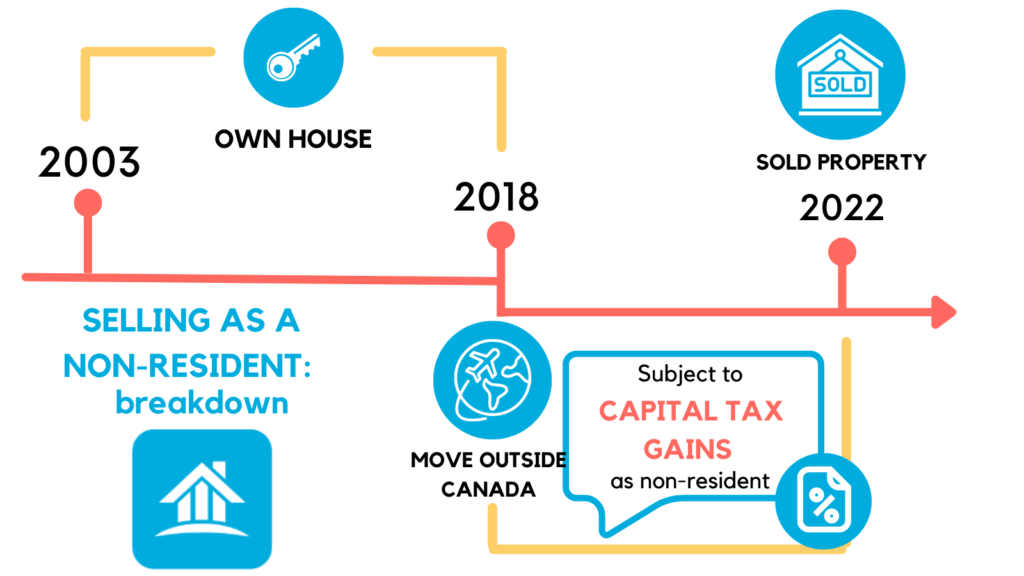
You’re generally liable to capital gains taxes in the years you’re a non-resident. For example, suppose you owned a home from 2003 to 2022.
- The home was your principal residence between 2003 and 2018.
- In 2018, you became a non-resident and moved out of the country.
- In 2022 you sold your Canadian home as a non-resident.
In this case, you’re likely liable to capital gains tax between 2018 and 2022 because the property was no longer your principal residence in these years.
Once the home is sold, you need to inform CRA of the sale within ten days after the sale closes. You make this notification through Form T2062. If you don’t, there’s usually a penalty of up to $2,500. The form requires you to estimate your capital gain or loss on the sale.
The property buyer may also assist in the tax collection process by withholding taxes from the due proceeds. This amount could be 25% of the purchase price being held up for months. So it’s best to be prepared for such a situation from a cash flow perspective.
When you sell your home as a non-resident, speak with a tax professional to understand your tax obligations. It will prevent surprises from hitting you in the face when you least expect them — like a 25% withholding tax on the sale of your Canadian property.

Repay Your Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP)
The Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP) lets Canadians withdraw from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSP) to buy or build their home.
Currently, the withdrawal is limited to $35,000, and you must repay the amount within 15 years. If you don’t repay the amount, it’s included into your RRSP income on your tax return, which could have significant income tax consequences.
If you choose to leave Canada, you need to repay your HBP or face an income inclusion for the amount. The balance of your HBP is payable on the earlier of:
- Before the date you file income tax for the year you become a non-resident;
- Sixty days after leaving Canada.
So if you’re planning to emigrate from Canada, it’s essential to ensure you have the funds ready to return whatever you borrowed from your RRSP to purchase your home. Otherwise, you’ll be on the hook for a lot of taxes!
Leaving Canada has many tax implications. Selling your home after you’ve left the country complicates this situation. If you’re leaving Canada or selling your home as a non-resident, it’s vital to speak with a tax professional and experience realtor to understand the implications of your decision.




